Introduction
The offshore wind industry is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by advances in engineering, floating platform technology, and digital innovation. Japan, with its vast maritime Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and ambitious renewable energy targets, is uniquely positioned to lead in next-generation offshore wind solutions. This comprehensive guide explores the latest technologies shaping the sector — from the fundamental mechanics of wind power to specialized floating platform designs, demonstration projects, and emerging trends beyond 2030. Through in-depth technical insights and global case studies, we connect the dots between innovation, cost competitiveness, and commercial viability, offering a complete view of how offshore wind will evolve in Japan and around the world.
1. Understanding How Offshore Wind Works
Offshore wind power is a complex, integrated system that combines turbine engineering, power generation principles, grid connection, and environmental considerations. This article breaks down the energy conversion process, blade design optimizations for higher efficiency, environmental and site constraints, and the key differences from onshore wind systems. It also covers global deployment trends and Japan’s adoption path, providing a foundation for both newcomers and industry experts.
👉 [Detailed Guide: How Wind Power Works (Basic)]
👉 [Detailed Guide: How Wind Power Works (Practice)]
2. Fixed-Bottom vs Floating Foundations
Fixed-bottom foundations are optimal for shallow waters, while floating structures are essential for depths over 50 meters. This article explains the structural principles of floating foundations, mooring systems, stability mechanisms, and operational characteristics that differ from fixed-bottom projects. It also reviews global adoption patterns and Japan’s strategy for adapting to its unique marine conditions.
👉 [Basics of Floating Offshore Wind Structures]
3. Floating Platform Types & Selection Criteria
From Spar buoys to Semi-submersibles and Tension Leg Platforms (TLPs), each floating platform type has distinct engineering principles, weather resistance, fabrication cost, and site suitability. This article compares their stability theories, mooring configurations, and maintenance requirements, providing clear guidance for developers and engineers making design and procurement decisions.
👉 [Key Floating Platform Designs & Features]
4. From Demonstration to Commercialization: Global & Domestic Case Studies
To cut costs and standardize technology, both domestic and international players are developing shared technical frameworks for floating wind. This article highlights initiatives like FLOWRA’s design guidelines, construction standards, and O&M optimization efforts, along with real-world examples of supply chain collaboration to boost competitiveness.
👉 [Floating Offshore Wind Technology Standardization Efforts]
Japan’s floating offshore wind industry is reaching a historic milestone. For the first time, Japanese floating foundation technology will be demonstrated overseas. Announced on June 13, 2025, in Rio Grande do Sul, the Aura Sul Wind Project, led by JB Energy (Japan Blue Energy), will deploy the innovative Raijin Float in combination with the world’s largest offshore wind turbine, the MySE 18MW. This marks a turning point as Japanese technology steps onto the international stage.
👉 Aura Sul Wind project in Brazil
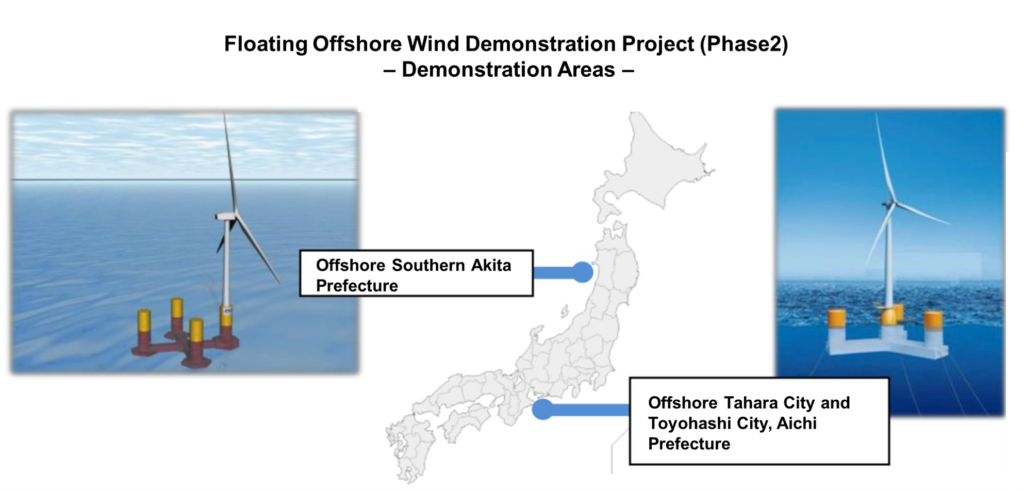
5. Japan’s NEDO Phase 2 Demonstration Projects
NEDO Phase 2 projects in Akita and Aichi mark a crucial stage in validating commercial-scale floating wind. The article covers large-turbine integration, automated mooring monitoring, optimized service vessel operations, and the cost assessment frameworks being tested. It also analyzes how results could influence Japan’s regulatory design and business models.
👉 [NEDO Phase 2 Demonstration Overview]
6. Comparing Floating Wind Demonstration Projects Worldwide
By examining overseas leaders like Hywind (Scotland) and Floatgen (France) alongside Japan’s Kamaishi and Goto Island pilots, this article compares technology performance, cost structures, and grid connection challenges. It distills key lessons for scaling up and outlines design refinements needed for competitive commercialization.
👉 [Floating Wind Demonstration Case Studies]
7. Tackling Japan’s Extreme Offshore Conditions
Japan’s EEZ features some of the deepest waters and harshest conditions in the world, with depths exceeding 500–1,000 meters, strong winds, high waves, and typhoon exposure. This article details the technological adaptations in floating structures, mooring systems, durable materials, and operational planning, as well as the regulatory and spatial coordination measures under development.
👉 [Extreme Conditions Testing & EEZ Deployment]
8. Technology Innovation: Floating Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT)
Floating VAWTs offer inherent advantages such as omnidirectional wind capture and lower center of gravity for improved stability. This article explores optimized blade geometry, balancing efficiency with structural strength, and the potential for reducing installation costs. It also reviews demonstration-stage challenges and assesses commercial viability.
👉 [Floating VAWT Development & Potential]
9. Post-2030 Floating Wind Trends & Outlook
The post-2030 era could see the rise of 20MW-class turbines, AI- and IoT-driven autonomous O&M, hybrid floating wind-plus-solar systems, and offshore green hydrogen production (Power-to-Gas). This article outlines the most promising technology trajectories, market forecasts, and policy implications for Japan and the global floating wind industry.
👉 [Future Trends in Floating Offshore Wind]
Conclusion
Offshore wind is no longer just a promising technology — it is becoming a cornerstone of global energy transition strategies. In Japan, the combination of deep-water expertise, innovative floating structures, and large-scale demonstration projects is accelerating the path toward commercialization. As the industry moves into the post-2030 era, developments such as 20MW-class turbines, hybrid renewable systems, and offshore hydrogen production will redefine what’s possible. For investors, developers, and policymakers, understanding these technologies and their market implications is essential to staying ahead. By integrating engineering excellence with strategic planning, Japan can not only meet its renewable energy goals but also set new global benchmarks for floating offshore wind deployment.
Don’t forget to explore more in our [Technology & Innovation] category and related featured articles.
📘 Browse the Technology & Innovation Articles
Japan’s offshore wind is no longer constrained by ambition — but by viability.📘 DeepWind Premium Report
A decision-oriented report synthesizing commercial viability, cost/revenue misalignment, supply-chain constraints, and Round 4 implications.
View the report (Gumroad)

- 🔍Market Insights – Understand the latest trends and key topics in Japan’s offshore wind market
- 🏛️Policy & Regulations – Explore Japan’s legal frameworks, auction systems, and designated promotion zones.
- 🌊Projects – Get an overview of offshore wind projects across Japan’s coastal regions.
- 🛠️Technology & Innovation – Discover the latest technologies and innovations shaping Japan’s offshore wind sector.
- 💡Cost Analysis – Dive into Japan-specific LCOE insights and offshore wind cost structures.