Japan is accelerating the deployment of offshore wind power, and one of the most symbolic projects in this effort is the Nagasaki Saikai Enoshima Offshore Wind Project. This initiative is part of the Japanese government’s 2nd round of offshore wind power auctions—commonly known as “Round 2”—and represents a critical step toward achieving the national targets of 10 GW of offshore wind capacity by 2030 and 30–45 GW by 2040.
With a total planned capacity of 420 MW, the project will significantly contribute to the decarbonization of Japan’s energy mix through fixed-bottom offshore wind power. It is also expected to drive regional industrial development and economic revitalization. This article provides a detailed overview of the project, including its schedule and estimated CAPEX & OPEX.
➡ For an overview of all ten Promotion Areas as of 2025, see:
Promotion Areas for Offshore Wind in Japan – 2025 Overview
1. Project Overview
The Nagasaki Saikai Enoshima Offshore Wind Project is a fixed-bottom offshore wind farm, strategically positioned to leverage strong wind resources in the East China Sea. Developed under Japan’s public auction system, this project aligns with the government’s goal of expanding offshore wind energy as a core component of the country’s energy mix.
| Project name | Nagasaki Saikai Enoshima Offshore Wind |
| Developer | mirai enoshima LLC |
| stakeholders | Sumitomo Corporation TEPCO |
| Location | Offshore saikai enoshima, nagasaki Prefecture |
| Type | Fixed-bottom Offshore Wind Power |
| WTG | vestas |
| Price | 22.18 JPY/ kWh |
| Capacity | 420 MW (15 MW × 28 turbines) |
| Start of Construction | november 2027 |
| Operation Period | august 2029 – February 2055 |
2. Location
2-1. Sea & Geographical Features
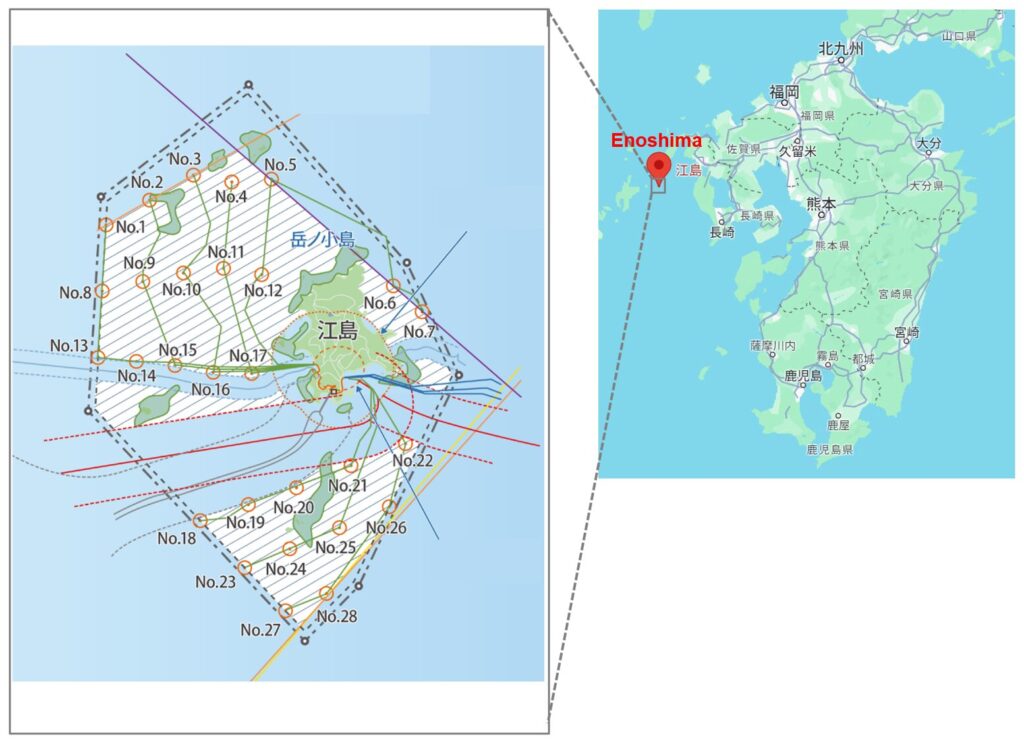
The waters off the coast of Enoshima, Nishisonogi Islands, Nagasaki Prefecture. The supply price is high 22.18 yen/kWh. The design also takes into account the risk of high waves during typhoons and bad weather.
2-2. Port Infrastructure & Grid Connection
Construction and installation will be carried out using large barges, etc., based in the nearby ports of Sasebo and Nagasaki. The plant will be connected to Kyushu Electric Power’s transmission system (such as the West Kyushu Main Line) and electricity will be transmitted to areas of demand on the Kyushu mainland.
3. Project Overview
3-1. Consortium Members
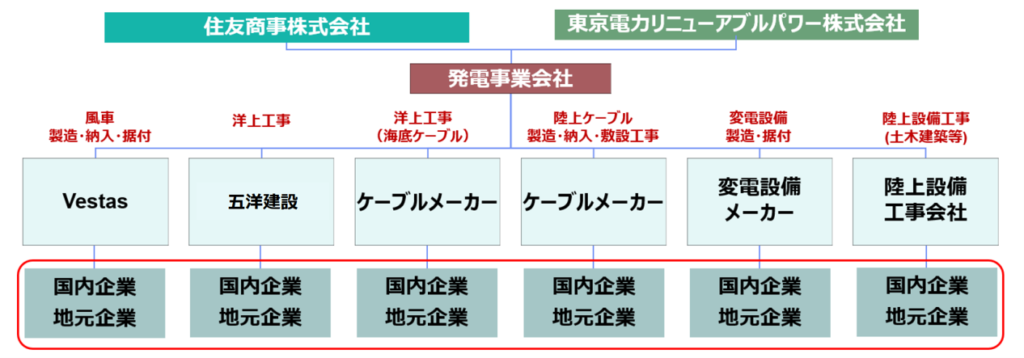
Sumitomo Corporation
- Proven track record in the development and operation of offshore wind projects in Europe, with a total of 1.9 GW currently in operation or under construction.
TEPCO Renewable Power
- A subsidiary of Japan’s largest electric utility, with extensive experience across hydropower, wind, and solar, maintaining a total installed capacity of approximately 10 GW.
3-2. Project Implementation Structure
Construction Phase
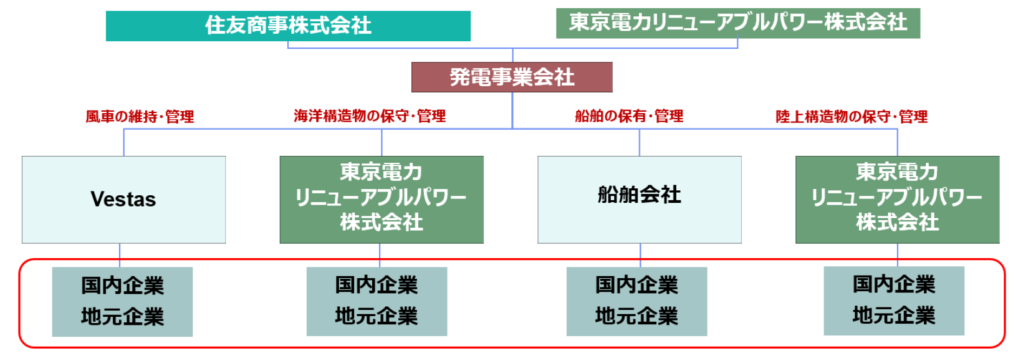
Operation Phase
4. Project Schedule
4-1. Overall schedule
Development & Design Phase (2024–2025)
- March 2024: Award of public auction
- Environmental impact assessment, wind, wave, and seabed geological surveys
- Local stakeholder consultations and coordination
- Wind farm certification and submission of construction plan
Construction Phase (2025–2029)
- January 2025: Construction of onshore substation and transmission infrastructure
- October 2027: Installation of offshore foundations and cables
- January 2029: Assembly and installation of wind turbines
Operation & Maintenance Phase (2029–2054)
- Turbine maintenance: Vestas
- Operation management (BOP): TEPCO Renewable Power
Decommissioning & Repowering Phase (Post-2054)
- Decommissioning plan at end of wind farm’s service life
- Potential repowering depending on future energy policy
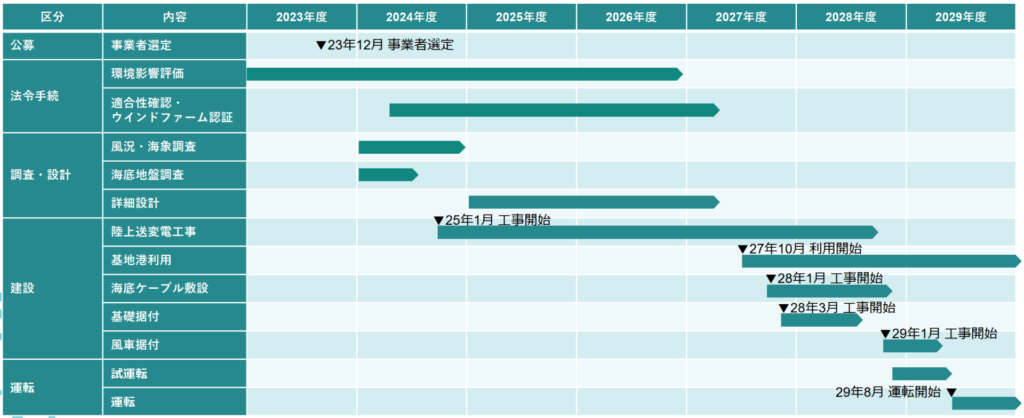
Source: Public document by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, METI
4-2. EIA status
| Prefecture | Project name | Developer | EIA Stage | Project Scale | Last updated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nagasaki | (Tentative name) Offshore Wind Power Project off Ejima, Saikai City | Miraie Enoshima G.K. | Draft EIA Statement | Total output: 420 MW Turbine capacity: 15 MW per unit Number of turbines: 28 units | November 11, 2025 |
| Nagasaki | (Tentative name) Saikai Offshore Wind Power Project | Electric Power Development Co., Ltd. (J-POWER), Sumitomo Corporation | Method Statement | 313.5–392 MW; up to 33 turbines (for 9.5 MW each) or up to 28 turbines (for 12–14 MW class) | Aug 26, 2025 |
| Nagasaki | (Tentative name) Saikai Eshima Wind Power Project | Japan Renewable Energy Corporation | Project Terminated | Up to 299.5 MW (approx. 24 turbines rated at 14–15 MW class) | Jul 3, 2025 |
5. LCOE and IRR Estimation
Evaluating the bankability of offshore wind projects requires close attention to key cost indicators such as LCOE (Levelized Cost of Energy) and IRR (Internal Rate of Return). However, in Japan’s Promotion Zones, detailed project-level cost information remains limited in publicly available materials. As a result, investors and developers often lack sufficient data to form a fully informed assessment.
To address this gap, DeepWind applies a proprietary cost model using representative site conditions for each project, including wind resource (capacity factor), water depth, distance to port, and distance to grid connection point. Based on these input parameters, we estimate CAPEX, OPEX, LCOE, and IRR in a consistent framework.
This approach allows us to provide a cross-project comparison of the relative economic positioning of Japan’s Promotion Zone projects.
▶ For the latest model assumptions and updated relative positioning, please refer to the cost analysis Pillar article below.
👉 Cost Realities of Japan’s Offshore Wind: Analyzing LCOE and IRR Across 12 Promotion Zones (Latest Edition)
Summary
The Nagasaki Saikai Enoshima Offshore Wind Project is a landmark development from Japan’s Round 2 offshore wind auctions. With a planned capacity of 420 MW, it will contribute significantly to the country’s offshore wind targets of 10 GW by 2030 and 30–45 GW by 2040, while also supporting regional industrial revitalization. Going forward, the project’s implementation will depend heavily on transmission system integration and onshore grid connection arrangements, which remain key elements in Japan’s offshore wind expansion.
To explore how this area compares nationally and understand Japan’s offshore wind roadmap, visit:
Promotion Areas for Offshore Wind in Japan – 2025 Overview —
your guide to Japan’s offshore wind Promotion Areas.
Explore more categories at DeepWind:
- 🔍Market Insights – Understand the latest trends and key topics in Japan’s offshore wind market
- 🏛️Policy & Regulations – Explore Japan’s legal frameworks, auction systems, and designated promotion zones.
- 🌊Projects – Get an overview of offshore wind projects across Japan’s coastal regions.
- 🛠️Technology & Innovation – Discover the latest technologies and innovations shaping Japan’s offshore wind sector.
- 💡Cost Analysis – Dive into Japan-specific LCOE insights and offshore wind cost structures.



