Introduction
In this final installment, we’ll explore the innovations expected to shape floating offshore wind after 2030 and the market dynamics likely to drive growth. With net-zero ambitions rising globally, floating wind is poised for new phases of evolution—larger turbines, smarter platforms, hybrid energy hubs, and advanced O&M. Let’s outline the strategic directions engineers may wish to consider.
If you want to first grasp the full picture of floating offshore wind—covering market context, platform types, cost structure, regulations, pilot projects, and the post-2030 outlook—see our pillar article.
👉 Floating Offshore Wind: Structure, Economics, and Market Context (Pillar)
This article takes a deep dive into this specific topic, but if you’re looking for a comprehensive overview of offshore wind technologies, check out our full summary article here:
👉 Offshore Wind Technology 2025: Foundations, Floating Wind, Turbines, and Innovations
1. Ultra-Large Turbines & Modular Towers
IEA forecasts that by 2030, 20–25 MW-class floating turbines with 200–250 m rotors will become common, potentially boosting annual energy yield by 30–40% and reducing LCOE. Modular tower segments for port-side assembly are also expected to cut logistics costs by up to 20%, which could be especially valuable in regions with smaller harbors.
2. Hybrid Platforms & Active Vibration Control
Hybrid platforms combining SPAR, TLP, and semi-sub designs are anticipated to gain traction. Optimized steel-concrete mixes and sensor-actuator-based active tuned mass dampers could reduce wave-induced motions by over 30%, potentially extending component fatigue life by 20%.
3. Advanced Materials & Manufacturing Innovations
Emerging materials like nano-cellulose composites and high-strength carbon fibers, combined with 3D-printed joints and on-site assembly jigs, are expected to halve assembly time. Self-healing polymers and advanced anti-corrosion coatings may extend maintenance intervals by 20–30%, lowering O&M costs.
4. Digital Twins & Real-Time Optimization
Plant-wide digital twins, linked to real-time weather and wave data, are expected to allow AI-driven control adjustments—forecasting extreme loads and optimizing performance. Failure prediction accuracy could exceed 90%, with O&M cost reductions up to 35%.
5. AI & Robotics for Unmanned Inspection & Repairs
Offshore drone fleets and autonomous ROVs, combined with AI image analysis to detect cracks or corrosion instantaneously, are poised to become standard practice. Robotic arms for blade cleaning and minor repairs may reduce human intervention by over 60%, significantly cutting O&M expenses.
6. Offshore P2G & Integrated Energy Hubs
Offshore power-to-gas systems—integrating electrolyzers and ammonia synthesis units—are projected for 5–20 MW-scale demonstrations by 2030, enabling on-platform green hydrogen and ammonia production. This could help optimize both LCOE and LCOH and offer new revenue streams.
7. Global Market & Financing Trends
IEA expects floating wind capacity to reach 50 GW by 2030, with investment flows growing 20% annually to $30–40 billion. Beyond Europe and North America, Asia-Pacific markets in South Korea, Taiwan, and Australia are emerging, likely driving greater use of green bonds and ESG-linked loans.
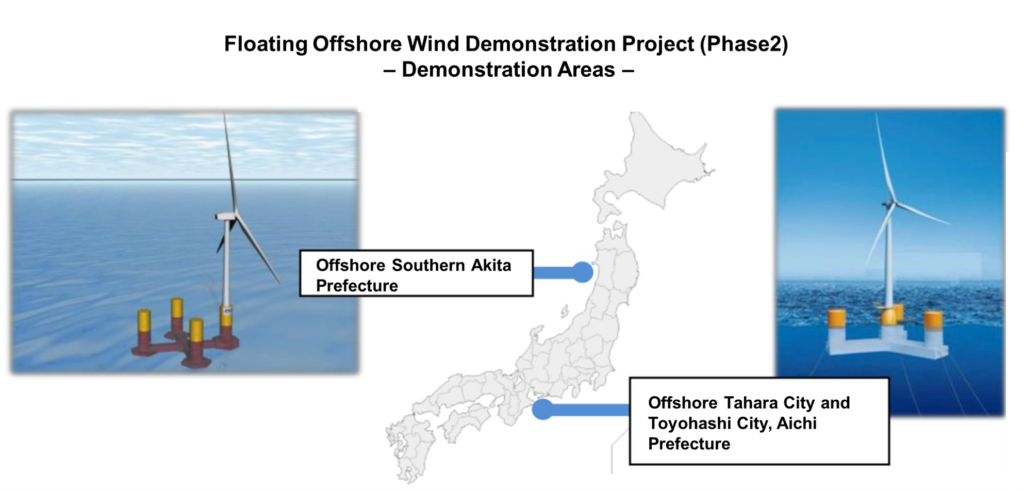
8. Japan Market Opportunities & Considerations
In Japan, expanding floating wind is seen as essential for achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. Urgent measures include extending installations into the EEZ and refining FIT and auction schemes. At the same time, deepening regional ports, developing co-existence models with fisheries, and strengthening typhoon and seismic resilience must proceed in parallel. These challenges demand not only technical solutions but also broad stakeholder collaboration.
9. Career & Skill Strategies for Industry Professionals
Through the 2030s, floating wind will rely on a blend of structural analysis, CFD, control engineering, data science, and robotics. Industry professionals are encouraged to engage in university and research collaborations, participate in OJT programs, and leverage digital twin workshops to build the interdisciplinary expertise needed for “offshore wind engineering” careers.
Conclusion
After 2030, we expect simultaneous advances in ultra-large turbines, hybrid platforms, digital twins, Power-to-Gas, and AI/robotic O&M. In Japan, success will hinge on combining technical innovation with effective stakeholder coordination. By embracing these strategies, industry professionals and organizations can propose world-leading solutions and drive the next wave of floating offshore wind development.
Floating offshore wind cannot be understood through technology alone. A comprehensive view—spanning market drivers, cost structures, regulations, pilot projects, and the post-2030 roadmap—is consolidated in our pillar article.
👉 Floating Offshore Wind: Structure, Economics, and Market Context (Pillar)
For a broader look at offshore wind technologies and future innovations, make sure to explore our comprehensive summary article:
🌊 Offshore Wind Technology 2025: Foundations, Floating Wind, Turbines, and Innovations
Japan’s offshore wind is no longer constrained by ambition — but by viability.📘 DeepWind Premium Report
A decision-oriented report synthesizing commercial viability, cost/revenue misalignment, supply-chain constraints, and Round 4 implications.
View the report (Gumroad)

- 🔍Market Insights – Understand the latest trends and key topics in Japan’s offshore wind market
- 🏛️Policy & Regulations – Explore Japan’s legal frameworks, auction systems, and designated promotion zones.
- 🌊Projects – Get an overview of offshore wind projects across Japan’s coastal regions.
- 🛠️Technology & Innovation – Discover the latest technologies and innovations shaping Japan’s offshore wind sector.
- 💡Cost Analysis – Dive into Japan-specific LCOE insights and offshore wind cost structures.